Types of Operating Systems: An Overview
An operating system (OS) is the software that manages and controls all the resources of a computer system. It acts as an interface between the hardware and the users of a computer system. There are several types of operating systems, each designed to meet specific needs and requirements. In this blog, we will explore the different types of operating systems, including batch, time-sharing, distributed, network, and real-time operating systems.
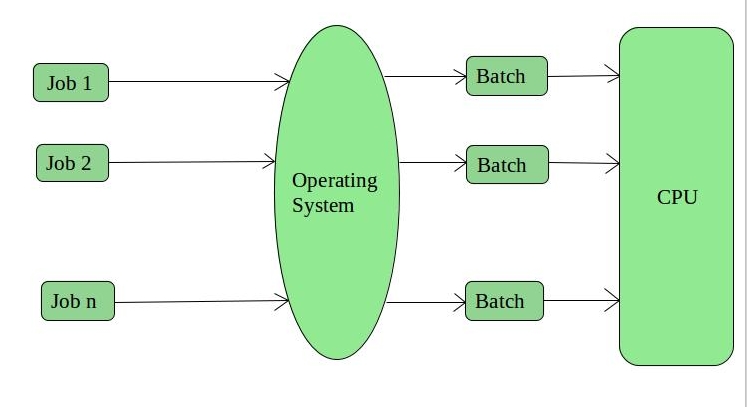
Batch Operating System:
Batch operating systems are designed to process a large number of jobs in a batch. In this type of system, jobs are collected together and processed as a single unit, with no interaction between the user and the computer during the processing. The advantage of batch processing is that it reduces the overhead of the operating system, making it more efficient.
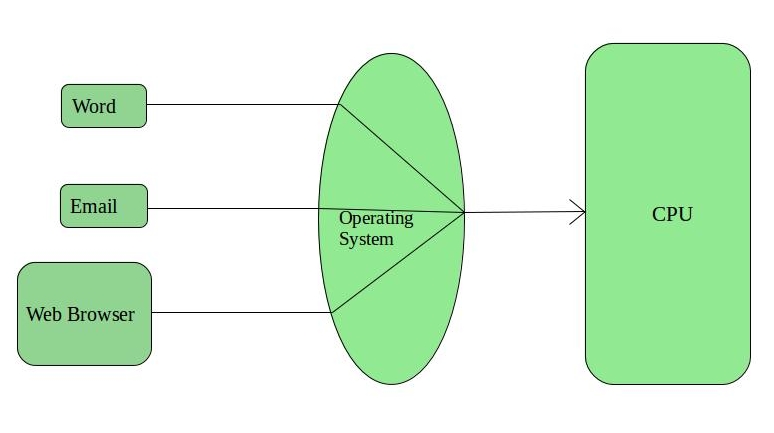
Time-Sharing Operating System:
Time-sharing operating systems, also known as multi-tasking operating systems, allow multiple users to access the computer system simultaneously. Each user interacts with the computer through a terminal and can run multiple programs at the same time. Time-sharing systems use time slicing techniques to allocate the CPU time to each user.
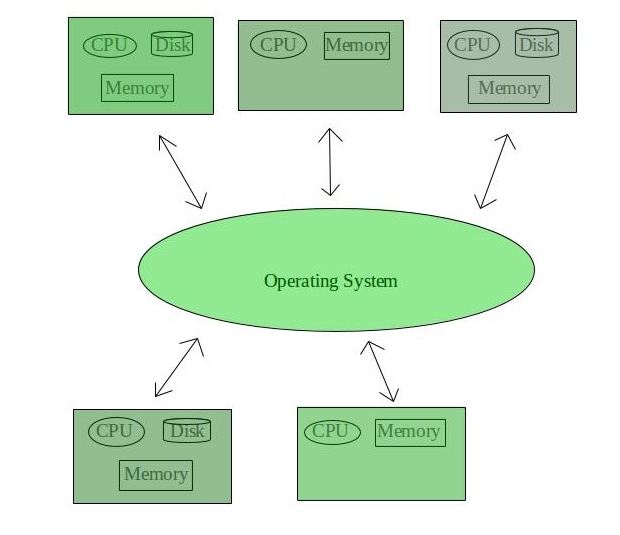
Distributed Operating System:
A distributed operating system distributes the resources of a computer system among multiple computers connected over a network. In a distributed system, each computer works together to perform a specific task, with each computer having its own operating system. The advantage of a distributed system is that it provides a higher level of reliability, as the failure of one computer does not affect the functioning of the rest.
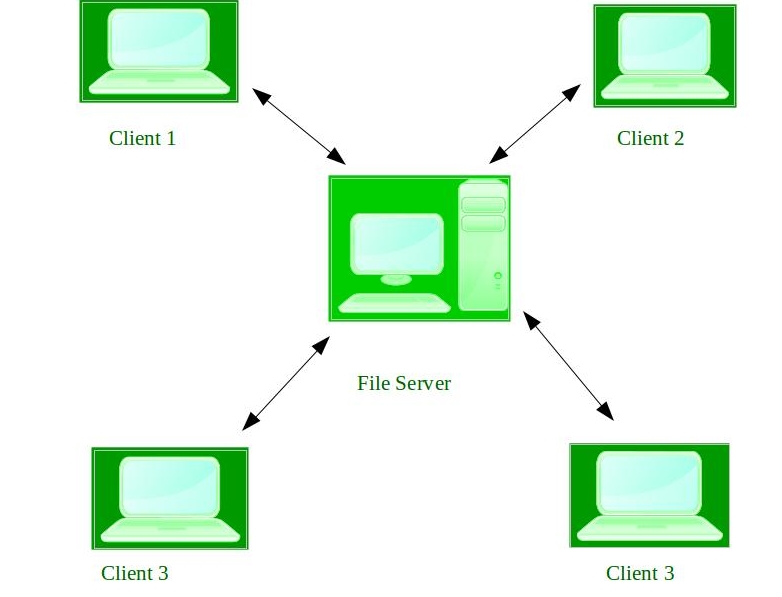
Network Operating System:
A network operating system provides services to support the sharing of resources and information among multiple computers connected over a network. Network operating systems include features such as file and printer sharing, user authentication, and network management. They are designed to allow multiple users to access shared resources, such as files and printers, from different computers.
Real-Time Operating System:
A real-time operating system is designed to process real-time data and respond to events within a specified time frame. Real-time systems are used in applications where it is important to respond quickly to events, such as in aerospace, military, and medical systems. In a real-time system, the operating system must be able to process data in real-time, without any delays.
In conclusion, each type of operating system is designed to meet specific needs and requirements. Whether it is a batch system for efficient processing, a time-sharing system for multiple user access, a distributed system for reliable operation, a network system for shared resources, or a real-time system for fast response, it is important to choose the right operating system to meet the specific needs of the computer system.