Types of Transmission Media:
In data communication terminology, a transmission medium is a physical path between the transmitter and the receiver i.e. it is the channel through which data is sent from one place to another. Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types:
1. Guided Media:
It is also referred to as Wired or Bounded transmission media. Signals being transmitted are directed and confined in a narrow pathway by using physical links.
Features:
- High Speed
- Secure
- Used for comparatively shorter distances
There are 3 major types of Guided Media:
(a) Twisted Pair Cable –
It comprises of 2 independently protected channel wires twisted about one another. For the most part, a few such coordinates are packaged in a defensive sheath. They are the most broadly utilized Transmission Media. Wound Pair is of two sorts:
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP):
UTP consists of two insulated copper wires twisted around one another. This type of cable has the ability to block interference and does not depend on a physical shield for this purpose. It is used for telephonic applications.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP):
This type of cable consists of a special jacket (a copper braid covering or a foil shield) to block external interference. It is used in fast-data-rate Ethernet and in voice and data channels of telephone lines.
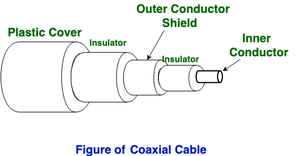
(b) Coaxial Cable –
It has an external plastic covering containing a protection layer made of PVC or Teflon and 2 equal guides each having a different protected insurance cover. The coaxial link communicates data in two modes: Baseband mode(dedicated link transmission capacity) and Broadband mode(cable transfer speed is parted into discrete reaches). Link televisions and simple broadcasting companies generally utilize Coaxial links.
(c) Optical Fiber Cable –
It uses the concept of refraction of light through a core made up of glass or plastic. The core is surrounded by a less dense glass or plastic covering called the cladding. It is used for the transmission of large volumes of data.
The cable can be unidirectional or bidirectional. The WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer) supports two modes, namely unidirectional and bidirectional mode.
(d) Stripline
Stripline is a cross over electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium created by Robert M. Barrett of the Aviation based armed forces Cambridge Exploration Center during the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest type of the planar transmission line. It utilizes a leading material to communicate high-recurrence waves it is likewise called a waveguide. This directing material is sandwiched between two layers of the ground plane which are generally shorted to give EMI invulnerability.
2. Unguided Media:
It is also referred to as Wireless or Unbounded transmission media. No physical medium is required for the transmission of electromagnetic signals.
Features:
- The signal is broadcasted through air
- Less Secure
- Used for larger distances
There are 3 types of Signals transmitted through unguided media:
(i) Radio waves –
(ii) Microwaves –
(iii) Infrared –
